How to become an Electrician
Learn how to become an electrician from the team of online college and scholarship experts at The College Monk.
How to Become an Electrician
This article provides in-depth information about what an electrician is, what electricians do, degrees for electricians, steps to become an electrician, and much more.
Electricians are highly skilled trade professionals who are trained to handle a wide variety of issues associated with electrical power, lighting, and control systems.
If you’re interested in becoming an electrician, this article will give you the information you need about schooling, courses to take, required experience, and more.
What does Electrician do ?
An electrician has many duties, including repairing, maintaining, and installing electrical equipment.
For example, electricians read blueprints that reveal the location of outlets, circuits, and other equipment, and they make repairs or update recommendations for the system based on that blueprint.
Electricians also keep their communities safe by preventing and responding to dangerous electrical situations.
Some of the main tasks that an electrician has to handle are:
- Adding, maintaining, and replacing circuit breakers, fuses, and wires.
- Finding and replacing faulty wiring or aged wiring that could pose a safety hazard.
- Planning the layout and installation of wiring through an entire building or series of buildings.
- Reading blueprints to learn where circuits, outlets, panel boards, and other electrical components are to be found.
- Reviewing other electricians’ work in a building and making sure it meets the safety standards set out in the national electrical code.
- Teaching and appraising apprentices.
Depending on licensing and experience, electricians are categorized one of the following ways:
Journeymen electricians
After completing an apprenticeship, you can become a journeyman electrician. A journeyman electrician is a licensed electrician that can work without supervision, though they will often still work under a master electrician.
A journeyman electrician can become a master electrician only after they’ve had about two years of on-the-job experience.
Master electricians
Once a master electrician is fully licensed, they can oversee apprenticeships for journeymen electricians, lead job sites, and supervise electrical teams.
While specific qualification requirements vary from state to state, licensing requirements typically mandate that the candidate pass an exam.
Master electricians may work in conjunction with electrical engineers to handle complex projects.
Independent electrical contractors
Electrical contractors are freelancers or small business owners who work with hired teams of electricians to complete larger jobs. These electricians may work for residential or commercial clients.
While not every independent electrical contractor is a master electrician, they are required to have one on staff.
Specializations for electricians
Once electricians are licensed and certified, they can specialize in any of the following areas:
Residential
A residential electrician specializes in residential work. They focus on repairing, installing, and maintaining wiring, lighting systems, and electrical components in homes, apartment buildings, and other residential spaces.
Commercial
Commercial electricians work in commercial settings, such as factories and warehouses.
Since commercial buildings use dIfferent power systems than residential buildings, commercial electricians typically have a slightly different skill set than residential electricians.
To become a commercial electrician, you must complete a set number of commercial training hours in an electrician apprenticeship setting.
Industrial
Industrial electricians are similar to commercial electricians, except that they tend to work with larger machinery. For example, industrial electricians may specialize in working with machinery at manufacturing plants.
To become an industrial electrician, you must complete a period of training under the supervision of a licensed industrial electrician.
Additional concentrations to consider for an electrician
Here are some additional and even more specified concentrations to consider if you want to become an electrician:
Electrical drafters
Electrical drafters work with blueprints, create diagrams, and develop layout drawings for electrical equipment. They create diagrams for circuit boards and maintain and install electrical equipment.
Lineman
Linemen install and repair wires and cables that carry power from a powerhouse or substation to a particular destination.
Their job also includes building transmission towers and erecting utility poles.
Powerhouse, substation, and relay
These electricians work specifically with power-generating stations, substations, and in-service relays to make sure that the power grid stays up and running.
They're also responsible for inspecting and testing components of a station, repairing any problems, and maintaining equipment.
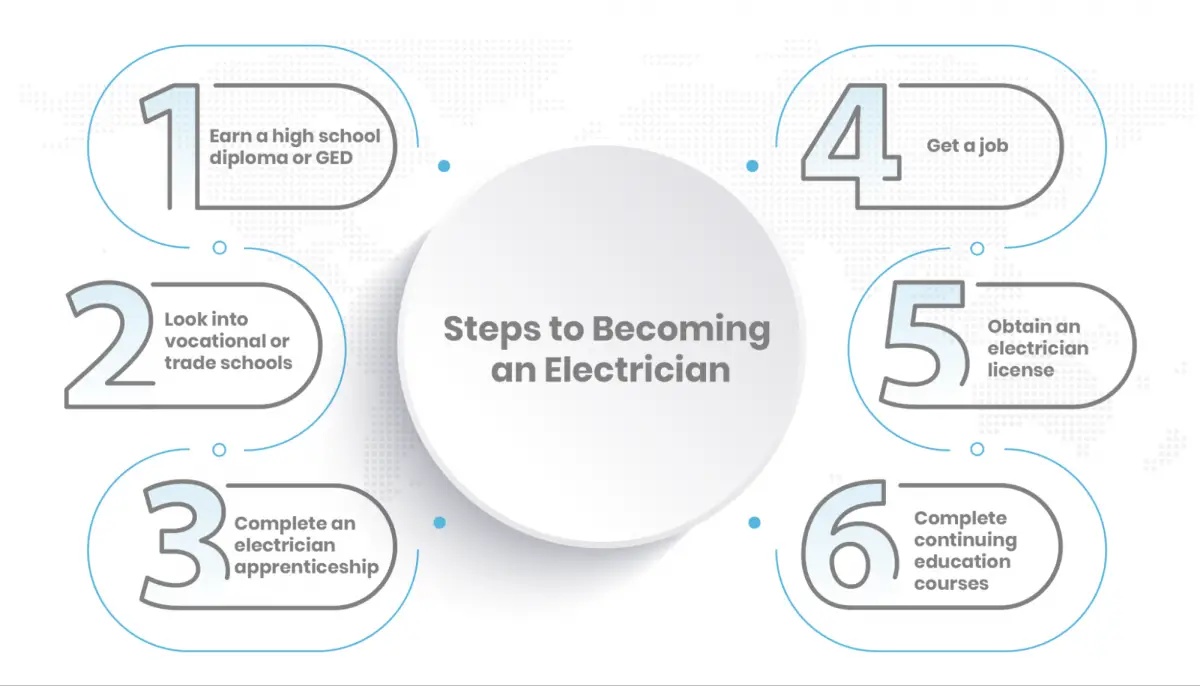
6 steps to becoming an electrician
If you’ve always dreamt of becoming an electrician, these six steps will get you into the field and help you land the job of your dreams:
Steps for becoming Electrician
1
Earn A High School Diploma Or GED
The first step to becoming an electrician is to obtain a high school diploma or GED. If possible, students who want to become electricians should take courses that offer some exposure to electrical principles, such as mathematics, physics, and other technical sciences.
Students should pay special attention to subjects like English because being an electrician requires one to know how to read technical documents. Fortunately, most vocational schools and local community colleges offer special programs exclusively for high school learners.
2
Look Into Vocational Or Trade Schools
Although you can become an electrician without attending an electrician school, many find that type of education helpful for their careers.
In addition to providing valuable training, attending a vocational school is an excellent way to make the certification process easier.
The exact educational path you take is up to you. Some students choose to attend a four-year university and study electrical technology. Others choose to get a career diploma via a trade school of their choice.
No matter which path you choose to take, you’ll find that the educational experience will provide a variety of classroom and real-world training opportunities.
Another benefit of attending an electrician school is that it may help you get licensed faster. Most states allow students to carry some of their study hours over and use them as some of the hours required to obtain journeyman licensing.
While each state has its own rules, the standard is that one year of formal education equals 1,000 hours of on-the-job experience.
If you’re planning on attending a trade school, consider browsing available student benefits.
3
Complete An Electrician Apprenticeship
Once a student decides on a career path, they must join an apprenticeship program sponsored by the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers (IBEW), National Electrical Contractors Association (NECA), or Independent Electrical Contractors (IEC).
These programs include both classroom and on-the-job training and take up to four years to complete. Here are a few common ways to find an apprenticeship program:
- Through a union. The Joint Apprenticeship & Training Committee (JATC) places students with local union employers and helps facilitate training throughout the course of the apprenticeship. Participating in a union apprenticeship does require you to join the IBEW.
- Through a trade school. If you attend a trade school, you can usually find an apprenticeship or job opportunity through your program. Talk to instructors and other students to learn more.
- Through a non-union. If you’d prefer not to join a union, you can find an apprenticeship through the Independent Electrical Contractors (IEC). The IEC has locations in most cities.
Requirements for an apprenticeship vary, but usually, students have to complete 144 hours of technical training and 2,000 hours of on-the-job training.
4
Get A Job
Your next step to becoming an electrician will be finding a job.
Electricians that have more than a year of training after an apprenticeship or classroom certification are known as helpers.
An electrician helper is usually assigned to work with one or more electricians on job sites. Helpers that start as apprentices will be given on-the-job training. Students with classroom certifications will work under the close supervision of a journeyman electrician.
5
Obtain An Electrician License
The requirements for licensure vary from state to state. However, electricians usually must pass a comprehensive examination that tests their knowledge of electrical theory, the national electrical code, local electric, and building codes.
6
Complete Continuing Education Courses
Best practices regarding electrical systems continue to change as technology develops. What was the best practice a few years back doesn't necessarily have to be the best practice today.
Electricians should continue learning via continuing education courses that keep them up-to-date on best practices and new trends in the electrical industry.
Types of degrees for an electrician
There are a few different educational paths available for people who want to become electricians. Let’s take a look at the different degree types that an electrician can obtain.
Electrician certificate
Electrician certification programs consist of basic courses designed to prepare students for apprenticeships.
Most certificates take up to a year to be completed. Students should make sure that their certificate program coursework is aligned with the latest version of the National Electrical Code.
Some apprenticeship programs accept credits earned in certificate programs.
Associate electrician degree
An associate degree is the most popular formal education option for electricians. It is a two-year degree program that offers specializations like renewable energy or industrial electrical technology.
Many associate degrees in electrical technology are offered as applied degrees. Applied degrees prepare students to start working immediately after graduation.
That said, some associate degrees offer general education courses that open doors to bachelor’s degree programs.
Apprenticeship
It's important for aspiring electricians to know that being an electrician apprentice is a must. Some apprenticeships will take formal education into account and apply academic credits to classroom hours.
Every electrical apprentice is required to complete 144 hours of classroom work and 2000 hours of hands-on training under the supervision of a licensed electrician.
During the electrician apprenticeship, the student will learn about blueprints, electrical code requirements, electrical theory, safety practices, and more.
After completing four to five years of training in an electrical apprenticeship program, apprentices can earn a journeyman license.
After several more years of competent work experience, an electrician is eligible to obtain a master electrician license.
What is the salary of an electrician?
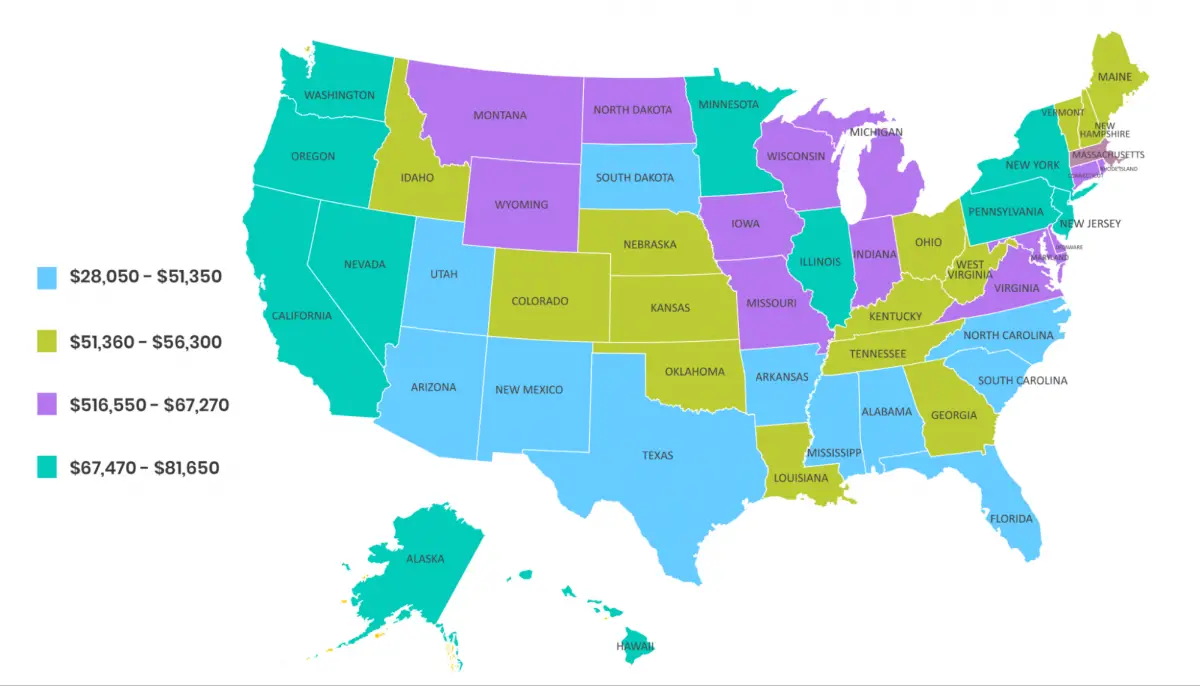
According to the Bureau of Labor Services (BLS), the average annual salary of an electrician is $55,200.
That said, it’s important to remember that the annual mean wage of electricians varies by state. For example, electricians working in New York, Massachusetts, California, and Washington may earn up to $78,000 per year.
Job growth of an electrician
According to BLS, employment opportunities for electricians are projected to grow by 10% between 2018–2028.
The fact that wiring is a must in homes, factories, and other businesses and will continue to be needed reassures that the job of an electrician will always be in demand.
Preparing yourself for a career as an electrician
Those that want to pursue a career as an electrician can prepare themselves in the following ways:
- Community college: Those that want to pursue higher education after high school can do so through community colleges that offer associate degrees in electrical technologies. It can take up to two years for the course to be completed.
- Trade schools: Trade schools offer certification and diploma courses for electricians. Some trade schools allow their students to start training as early as high school. Certifications and diploma courses take up to a year to complete.
- Military: Armed forces prepare service members for healthy civilian careers post-retirement. Those that want to pursue a career as an electrician will receive on-the-job training. They also enroll in courses that are designed to further their knowledge.
Skills to become an electrician
Following are the standout skills to become an electrician:
- Technical ability: Electricians need to be good at mathematics and critical thinking, as their job requires them to think technically. They should have both theoretical as well as practical knowledge. They should know how to read blueprints and must be up-to-date about codes.
- Manual dexterity: Electricians often have to be on their feet all day. Their work will require them to crawl through tight spaces and heavy materials, which requires electricians to have dexterity, physical stamina, and strength.
- Good customer service: Electricians work for customers. Therefore, it's essential that they provide good customer service. Often, people appreciate good customer service from a licensed electrician more than the product.
- Business savvy: Most electricians work independently. This requires them to be able to track the progress of their jobs, plan out payroll, and handle all other duties common to small businesses. Hence, it's important that electricians have the right knowledge about business.
Good communication skills: An electrician's job is technical in nature. But every job requires good interpersonal skills. Electricians must be able to understand electrical problems and effectively communicate them. Electricians also train apprentices, which requires good communication skills.

Conclusion
Being an electrician is an exciting, fast-paced, and rewarding career in an industry that’s projected to grow in the coming years.
Regardless of the career you choose to pursue, The College Monk is here to help you learn about the educational opportunities that will help you reach your goals.
Browse our selection of scholarships, financial aid packages, and online colleges today.
| Minumum Credit Score | Apply in as little as | Variable APR | Fixed APR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Not Available | 15 minutes or less | 2.95 | 4.74 | View disclosures |
 | 620 | 2 minutes | 5.38%-16.99%1 | 4.43%-16.99%1 | View disclosures |
 | Not Available | 15 minutes | 1.13% - 11.23%¹ (with autopay) | 3.50% - 12.60%¹ (with autopay) | View disclosures |