How to become a Nurse Practitioner
This article provides in-depth information into What is a Nurse Practitioner? What Nurse Practitioners do? Degrees for Nurse Practitioners, Steps to become Nurse Practitioner and much more.
A nurse practitioner has higher qualifications and training than a registered nurse. They are specialized in a particular area, such as family practice or pediatrics. Nurse practitioner prescribes medication, examines patients, diagnoses illnesses, and provides treatment to patients with or without a medical doctor sign on patient care decisions depending on the state. here is a detailed description of everything you need to know about becoming a nurse practitioner.
What does a Nurse Practitioner do ?
A nurse practitioner generally focuses on preventative and holistic care, with personalized treatment areas for each individual patient.
-
Prescribe specific medications, including the frequency and dose.
-
Diagnose and treat infections, wounds, and illnesses.
-
Direct and arrange diagnostic tests to be conducted such as x-rays and EKGs.
-
Record and examine the medical history, diagnoses, and symptoms of a patient.
-
Talk to patients about effectively managing their health, as well as helping in designing proper treatment plans.
-
Give care and direction to patients with regards to taking medication.
Steps for becoming a Nurse Practitioner
1
Become A Registered Nurse
To become a Nurse Practitioner you first have to complete all certification and get licensed required to become a Registered Nurse. There are several academic paths to become a Registered Nurse. An associate or bachelor’s degree from an accredited institution or a diploma from an approved vocational training program is needed to become a Registered Nurse.
2
Earn A Bachelor’s Degree
Earning a Master’s degree is mandatory to become a Nurse Practitioner. Most Colleges require Bachelor of Science in Nursing and some work experience before being accepted into Nurse Practitioner Program. Master’s degree level curriculum for a nurse practitioner follows the general course of study for an advanced practice registered nurse (APRN), with specialized NP education and training.
3
Obtain License And Certification
All 50 states require a license to become a Nurse Practitioner. To obtain License for Nurse Practitioner one must hold a master's degree in nursing and a valid state RN license and also pass a national certification examination.
4
Pursue Further Specialization
Obtaining additional credentials relating to a specific area of specialization increases the marketability of the candidate and opens up more opportunity. Examples of specialization as an APRN include Acute Care Pediatric Nurse Practitioner (ACNP), Adult-Gerontology Acute Care Nurse Practitioner (AG ACNP), Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) and Pediatric Nurse Practitioner (PNP).
Nurse Practitioner Degree Levels
Bachelors
A bachelor’s degree in nursing prepares students for a job as a registered nurse (RN) and also provides the educational foundation for a master’s degree in the field. Bachelor’s program in nursing is a mix of classroom and clinical learning where students are exposed to different topics and real-time training. Students take a variety of introductory courses on topics such as emergency care, health assessments, nutrition, public and global health, and current trends in nursing.
Pathophysiology
-
Problem-solving skill
-
Critical-Thinking skill
-
Advance Research skill
Objectives
-
Environmental factors linked to the development of certain illnesses
-
How various pathological changes can manifest in a patient or population
-
Critically evaluate medical journals
Pharmacological Concepts
-
pharmacological concepts
-
Advanced research skills
-
Nursing ethics
Objectives
-
Identify pharmacodynamics of the major classification of drugs
-
Administration of medications
-
Pathophysiologic conditions
Emergency Care and Safety
-
Environmental Emergencies
-
Medical Emergencies
-
Professional Rescuer CPR
Objectives
-
To understand the basics of first aid in an emergency setting
-
Advanced topics in disaster planning
-
Incident command, triage and oxygen therapy
Masters
A master of science in nursing is the minimum educational requirement to become a licensed nurse practitioner. Many programs combine professional core courses that dig deeper into subjects learned at the undergraduate level with clinical courses that focus on a particular specialty.
Philosophical and Ethical Basis for Nursing
-
Nursing Practice and Regulation
-
Promoting Moral Action in Nursing
-
Human Rights
Objectives
-
Provides a framework of nursing and ethics
-
Ethical issues affecting nurses
-
Effective ways to respond to issues
Clinical Pharmacology
-
Biochemical Mechanisms for Drug Toxicity
-
Drug Absorption
-
Pharmacokinetics
Objectives
-
Study of clinical uses of different drug groups
-
Bodily functions and responses to drugs
-
Side effects and drug interactions of commonly-administered drugs
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
-
Theory in disease prevention
-
Health Promotion Planning
-
Education for health
Objectives
-
To educate about different methods of preventive healthcare
-
Different ways of promoting health
-
Theories/models used in designing health promotion
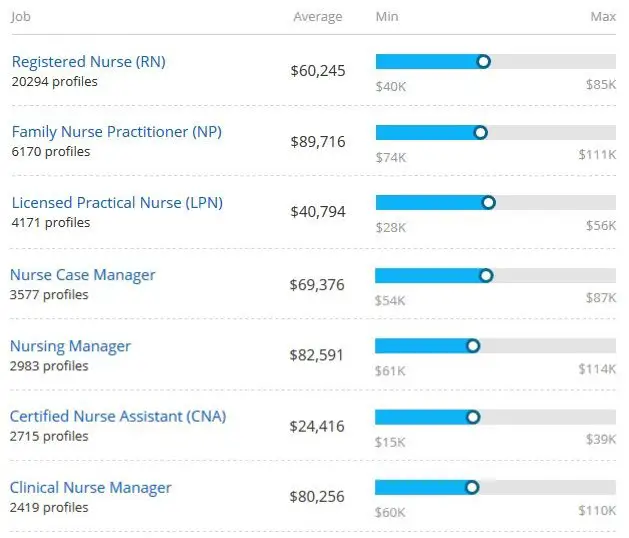
Salary of a Nurse Practitioner
As per the Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average annual salary of an NP is $ 114,000 approx. NP is one of the highest paying jobs in the country. The top 10% earn about $140,000 per year and the bottom 10% makes about $61,000 per year.
Job Growth of a Nurse Practitioner
The employment of nurse practitioners is projected to grow at 26% between 2018 and 2028 according to the Bureau of Labour statistics. Growth in employment will occur primarily because of the increased emphasis on preventive health care and the increasing population of aging people.
Concentration for becoming a Nurse Practitioner
Students pursuing degrees to become nurse practitioners will have to choose a concentration or specialty. In this part of their education, students will have to complete advanced courses, participate in workshops, and perform clinical work in the chosen field. Students can choose their choice of population - young, infants, and adults among others. Some of the most popular concentrations are as follows:
Adult-Gerontology Acute Care NP:
Adult-Gerontology Acute Care NP provides advanced nursing care to adults, older, and elderly patients with acute, chronic, and critical conditions. This concentration also focuses on adult life span management. In addition to a series of courses focused on pharmacology, health assessments, public policy in health care, and psychology, students will also have to complete up to 700 clinical hours.
Family Nurse Practitioner:
Also referred by the acronym FNP, is a registered nurse with specialized educational and clinical training in family practice. FNPs are particularly trained to work with both adults and children in the context of family practice. FNPs work with patients on maintaining health and wellness in the long run with a particular focus on preventive care. FNPs can either choose to work under the direct supervision of a physician or work independently. The work of an FNP is different than other specialties as FNPs monitor health and wellness as well as treat minor acute illnesses of people from all age groups. In addition to age diversity, many FNPs choose to work in underserved populations and communities. FNPs are responsible for compiling and tracking the health histories of one or more members of a family for a long period of time. Students pursuing FNP may need to complete up to 700 clinical hours along with courses covering key topics such as primary care for adolescents and adults, pediatric primary care, and advanced physiology among others.
Family Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse practitioner:
Also known as PMHNP works with patients who need mental health treatment. FPMNHPs are responsible for diagnosing, providing psychotherapy, and prescribing medication. They treat mental health patients with diagnosed disorders, those with family histories, or other factors that increase the likelihood of potential mental illness. In order to be an FPMHNP, students have to train in advanced coursework in areas of mental health disorders and psychiatric nurses along with practicums. The clinical hours and other requirements vary from school to school.
Neonatal Nurse Practitioner:
Neonatal NPs are advanced practice nurse that cares for premature and sick newborns in the neonatal intensive care units (NICU), emergency rooms, delivery rooms, or specialty clinics. NNPs assess, supervise, and manage the progress of their patients. They must have technical knowledge as their job requires them to use and monitor advanced medical equipment like incubators and ventilators. Students pursuing this concentration are required to complete extensive clinical work with about 1000 clinical hours and specialty courses in pediatric health, pharmacology, and nursing care for high-risk newborns. The job of an NNP is one of the highest-paid jobs in the country.
Pediatric Nurse Practitioner:
Also referred to as PNP, these nurses primarily work with children; right from infants to adolescents. PNPs focus on primary care, preventive health and growth, and development along with managing acute and chronic illnesses. Students pursuing this concentration need to complete 620 clinical hours in pediatric primary care and have to cover courses in advanced physiology, pharmacology, and pediatric care.
Standout Skills for a Nurse Practitioner
Following are the skills for being a successful NP:
Communication Skills: one of the most important skills to possess as an NP is good communication skills- both verbal and written. Good communication skill is vital to conveying messages with consistency, clarity, and compassion while working with both patients or medical staff. Good communication skills help build trust and create a strong bond with their patients.
Critical Thinking: An NP must be able to evaluate options to treat a condition and then be able to identify the best treatment suited that would bring out the best outcome while developing a treatment plan for their patients.
Organizational skills and time management: organizational skills go hand in hand with time management. An NP has a handful of duties to perform on a daily basis not to forget the last minute assignments and schedule changes. Knowing how to effectively chart EMRs, fill out paperwork, and easily adapt to a sudden change in schedule is of extreme importance.
Leadership Skills: one of the primary jobs of an NP is to lead other members of the nursing team like resident nurses and Licensed practical nurses. Leadership skills come into play here. NPs should be able to display great leadership skills.
| Minumum Credit Score | Apply in as little as | Variable APR | Fixed APR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Not Available | 15 minutes or less | 2.95 | 4.74 | View disclosures |
 | 620 | 2 minutes | 5.38%-16.99%1 | 4.43%-16.99%1 | View disclosures |
 | Not Available | 15 minutes | 1.13% - 11.23%¹ (with autopay) | 3.50% - 12.60%¹ (with autopay) | View disclosures |