How to become a Paralegal
This article provides in-depth information into What is a Paralegal? What Paralegals do? Degrees for Paralegals, Steps to become Paralegal and much more.
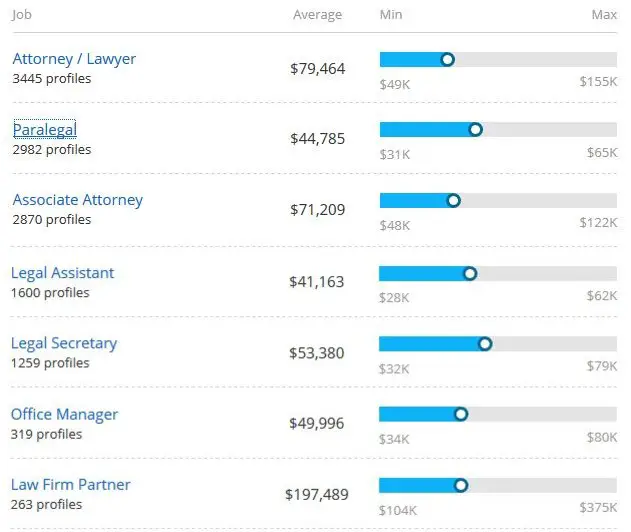
A paralegal, also known as a legal assistant helps attorneys with their tasks. They work in private law firms, government agencies or corporate legal offices. Paralegals help attorneys by planning for hearings, trials, and meetings and by keeping up communication with clients. becoming a paralegal, you are a legal professional who can perform numerous legal services, although tasks that are considered practicing law, such as representing a client in court, are prohibited.
What does a Paralegal do ?
Paralegals handle a broad range of administrative and research duties under the supervision of attorneys. The type of work a paralegal performs will depend upon his area of specialization and the specialty of the employing law firm.
-
Conducting legal research and collecting information on the case.
-
Assist attorney in preparing for trials, hearings, and closings.
-
Paralegals prepare presentations for the client.
-
Paralegals interview clients and summarize the testimony.
-
Paralegal draft legal documents.
-
Paralegals handle administrative tasks.
-
Paralegals deliver or retrieve documents from the courthouse.
-
They organize evidence and documents for attorneys to review.
-
They also manage schedules with witnesses and experts.
Steps for becoming a Paralegal
1
Choose A Speciality
Although most paralegals work as a generalist in a legal firm, some specialize in a particular sector of law. Deciding a specialty early will give time to the student to plan his career ahead and study subjects that are relevant to his/her carrier goals.
2
Earn A Bachelor’s Degree
Bachelor’s degree programs in paralegal studies and legal studies are both common. While some organizations will hire candidates with a two-year degree or certificate, the National Federation of Paralegals Association asserts that employers are increasingly requiring paralegals to possess a four-year degree and recommends that all aspiring paralegals work toward a bachelor’s degree.
3
Get Certified
Certification in paralegals is not mandatory; however, a student can stand out from the crowd by earning one. Some employer may require certification. Regardless, national surveys consistently show that certifications such as Certified Paralegals (CP) and Certified Legal Assistants (CLA) are used to determine and measure applicants’ abilities and skills. Paralegal organizations such as the National Association of Legal Assistants offer the CLA and CP certifications, which require passing a test and then pursuing continuing education.
4
Get An Internship
Chances of getting hired increases if the student has done an internship during its degree program. Students should look for an internship with a Law Firm, Corporation, Non-profit, or Government Agency during his/her degree program. Students will gain experience and have more opportunities for an entry-level job.
5
Get An Entry-level Job
Students should take help of their school’s career placement services and apply for a range of positions to maximize their chances of getting hired as a paralegal. Entry-level positions will give students an opportunity to begin practicing the techniques learned in school and allows for increased responsibilities down the road.
Paralegal Degree Levels
Associate
Earning an associate degree in paralegal studies gives students a strong understanding of the basic principles of the field as well as general education in math, science, social science, and English. Paralegal topics that are covered in most associate degree programs include an introduction to law, legal research and writing, civil litigation, and legal ethics.
Introduction to the Law
-
Role of the paralegal in a legal office
-
Basic aspects of American law
-
Practicing legal research and writing
Objectives
-
Provides a basic understanding of the law
-
The American justice system
-
Introduces the student to legal terminology and areas of law
Legal Research, Writing, and Civil Litigation
-
Determine jurisdiction and venue
-
Initiating and commencing a lawsuit
-
Client counseling
Objectives
-
Techniques necessary for handling cases from beginning to end
-
Introduction to Trial Practice
-
Basic Trial, Jury Selection
Professional Responsibility and Legal Ethics
-
regulations of paralegal conduct
-
Handling law office finances
-
Understanding of conflicts of interest
Objectives
-
Basic principles of practicing ethical law
-
Model Rules of Professional Conduct
-
Avoid unauthorized practice of law
Bachelors
A bachelor’s degree in paralegal studies is a four-year degree that trains students to perform the duties required of a paralegal through studies that focus litigation procedures, computer applications for law offices, ethics, various legal specialties, in addition to general education course requirements.
Criminal Law
-
Constitutional safeguards
-
Prosecution process
-
Federal sentencing guidelines
Objectives
-
Definitions and elements of crimes against persons and property
-
Various legal defences available to defendants
-
Interpret case decisions and precedent
Patents, Trademarks, and Copyrights
-
Different types of IP
-
Various types of infringement
- Defenses and remedies for infringement
Objectives
-
Overview of the various types of intellectual property
-
How to protect against infringement
- Defenses available for infringement both in the U.S. and abroad
Legal Document Preparation
-
Sales and service contracts
-
Real property contracts
-
Prenuptial agreements
Objectives
-
Learn practical skills of drafting and editing
-
Preparing legal documents through hands-on practice
-
Describe key elements of various civil pleadings
Masters
A master’s degree in paralegal studies is the highest level of education paralegal majors can pursue and designed for students who already have experience in the paralegal field, and who are looking to advance their career or focus their studies on one area of the law field.
US Legal Systems
-
Anatomy of a Civil Action
-
Jurisdiction Over Subject Matter and Person
-
American Constitutional Law
Objectives
-
Procedure and structure of the civil litigation process
-
Understanding of the structure of the American civil law
-
Specific areas of civil law
Mergers & Acquisitions
-
purchase of a publicly-held company
-
Allegations of misconduct
-
Deals involving non-U.S. companies
Objectives
-
Law-sensitive aspects of Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A)
-
Takeover defenses and Integration
- Rationale for a proposed transaction
Business Law
-
Formation of Contracts
-
International Trade
-
The Court System
Objectives
-
Basic understanding of the legal system
-
Business and business-related transactions
-
Writing Contracts
Certificate
Most paralegal certificates are for students who already have a bachelor’s degree or, at the very least, an associate degree. A post-baccalaureate certificate program can help you reach the next level of professionalism as it often lends itself to specialization in a specific area–in this case, paralegal studies.
Real estate
-
Broker and client contract
-
The withdrawal from sale clause
-
Agency, dual agency and agency disclosure
Objectives
-
Focuses on the buyer-seller relations
-
Title examinations and title insurance
-
Filing procedures
Legal ethics
-
Sources of Ethics Law
-
Reporting Misconduct
-
Civil and Criminal Liability
Objectives
-
Fundamental understanding of the professional codes of conduct
-
Laws dealing with the ethical obligations
-
Members of the legal profession
Family law
-
The Modern American Family
-
Marriage
-
Constitutional Right to Privacy
Objectives
-
Understand major themes and areas in family law
-
Legal efforts to improve child and family welfare
-
Policies and practices developed
| Minumum Credit Score | Apply in as little as | Variable APR | Fixed APR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Not Available | 15 minutes or less | 2.95 | 4.74 | View disclosures |
 | 620 | 2 minutes | 5.38%-16.99%1 | 4.43%-16.99%1 | View disclosures |
 | Not Available | 15 minutes | 1.13% - 11.23%¹ (with autopay) | 3.50% - 12.60%¹ (with autopay) | View disclosures |