How to become a Pilot
This article provides in-depth information into What is a Pilot? What Pilots do? Degrees for Pilots, Steps to become Pilot and much more.
Flying an aircraft requires much skill, practice, and a certain set of qualifications. A pilot needs to perform a list of nonexhaustive task on a day to day basis including running a check-up prior to taking off, briefing the crew about flight details, reporting any malfunctions, staying in constant touch with air traffic control, switching duties with the co-pilot to avoid exhaustion, monitoring all systems, filling the aircraft log among others.
To become a pilot, you must follow these steps and information:
- Gain a degree in-flight education
- Get experience through a minimum flying hours
- Gain FAA Pilot Certificate
- Earn a license
- Complete additional training
- Adance your career
|
Career Title |
Pilot |
|
Degree Requirements |
Flight education+ Certification |
|
Job Growth (2018- 2028) |
2% |
|
Experience required |
2 years |
|
Salary (2020) |
$137,501 |
|
How long to become a Pilot |
3-5 years |
|
Required Skills |
Interpersonal, Leadership, Communication, Stress management |
What does a Pilot do ?
Pilots fly fixed-winged aircraft and helicopters in order to provide transportation to passengers or cargo. Most aircraft usually require two pilots at a time during a flight. One of them is the captain and the other is called the co-pilot or the first officer. The captain is responsible for the safety of the aircraft, its passengers, and the cargo and is in command of the aircraft. The captain makes the final decisions and the co-pilot assists the captain. The pilots take turns flying the aircraft to avoid fatigue and safety hazards. While one of the pilots is operating the controls, the other is in constant communication with ground air traffic control and carries out the necessary paperwork and calculations. Sometimes, there can be three or more pilots on board to take turns flying the aircraft depending on the distance of the route and type of vessel they’re flying.
Steps for becoming a Pilot
1
Obtain A College Education
While a degree is not mandatory, employers prefer pilots who meet education requirements. There are college degree programs available for those who didn't learn to fly airplanes in the military. Commercial airlines prefer employees with a bachelor’s degree over those with associate’s degrees. Those that major in physics, mechanical engineering, computer science, or aerospace engineering have a better educational foundation for becoming a pilot. Commercial airlines prefer applicants who have taken up aeronautical engineering along with liberal arts classes. Flight school classes are typically taught by instructors who are certified by the federal aviation administration (FAA).

2
Gain Flying Hours
A pilot in training needs to log a minimum of 250 flying hours before being able to earn a pilot’s license. There are two ways to log these flying hours- pilots may fly with US Armed Forces where they will be familiarized with many different types of aircraft or they can become an instructor through the FAA. Flight schools help pilots in training earn their necessary flying hours by employing them as instructors.

3
Earn A License
Once the necessary flight hours are gained, the next step is to earn a pilot’s license. The applicant must be 18 years or above and can complete the rest of the requirements for a commercial pilot’s license from the federal government. Candidates must pass a physical and a written examination. While the physical examination ensures that the pilot has good vision, hearing abilities, and no physical impairments that might interfere with the performance of the flight. The written exam includes safety information and a skill test that is observed by an FAA-certified instructor.

4
Complete Additional Tests And Training
Additional tests and training are required depending on the type of pilot position. Certain airlines require their pilots to take psychological and intelligence tests. The FAA offers many different types of certifications such as airworthiness certificates and medical certificates.

5
Don Your Pilot Cap
Major airline companies prefer hiring pilots with a minimum of 4000 hours of flying hours. But pilots must begin somewhere. Hence, most pilots employed with commercial airlines work as co-pilots and obtain additional experience through this position. Alternatively, pilots may work in other industries to gain the required flying hours. These industries include emergency services, agriculture, or reforestation.

6
Work Your Way Up The Ladders
Pilots typically advance with experience. Pilots follow a ranking system of seniority. After gaining years of experience, typically anywhere between 5-15 years, a candidate is eligible to be promoted to the position of a pilot. Bigger airline companies have opportunities for even further promotion such as director of chief pilot position.

Pilot Degree Levels
Associate
In order to be able to take up the necessary training to become a pilot, a candidate has to either complete a four years bachelor’s degree or a two years associate degree. If a candidate doesn’t have the required fund to pursue a bachelor’s degree program, they can opt for an associate’s degree. Regional airlines do not require pilots to have a four years degree. An associate degree in Science with a focus on physics and mathematics will help you prepare better for the training. Commercial Airlines require two years of college or an associate degree in any field to be eligible for being a pilot. With an associate degree in a related field like Associate of Science Degree in Aeronautical Science & Technology will increase your chances of getting into good airlines.
Aircraft basic electricity, Electronics
-
Aircraft Wiring
-
Aircraft Generators
-
Avionics System
Objectives
-
Electrical and electronics systems of an aircraft
-
Technological advances in the field
-
Understanding of aircraft DC generators
Theory of Flight
-
blade flapping dynamics
-
rotor aerodynamic
-
examining the atmosphere
Objectives
-
To understand how planes fly in the air
-
Structure of the atmosphere and weather patterns
-
Principles of flight and air navigation
Aerodynamics
-
Fluid Mechanical Apparatus
-
Velocimetry
-
Laminar and Turbulence flows
Objectives
-
To study the behavior of air when a solid body moves through it
-
Formulate and apply appropriate aerodynamic models
-
Assess the applicability of aerodynamic models
Bachelors
Top airline companies demand a Bachelor’s degree in any field, given the condition that you have completed coursework in physics, maths, aeronautical engineering, and English. There is also a dedicated bachelor's program in aircraft operations, aviation, aeronautical engineering, or a related field. Candidates must pursue a bachelor's of science with a specialization in the field of aviation. Since major airlines pay better than regional airlines, it is recommended to pursue a four years bachelor’s degree. Those that do not pursue a bachelor’s of science but want to pursue a career as a pilot may be able to land him interviews with a smaller airline. The four-year bachelor’s degree program is a credential indicating that the candidate has the ability to think critically and complete the airlines’ unique education program. also to pursue the further step, ensure you learn about the time it takes to become a pilot to plan your career better.
Aviation Meterology
-
The Atmosphere
-
Heat Exchange Processes
-
Air Temperature, Density and Pressure
Objectives
-
Understanding of the physical properties of the atmosphere
-
Factors affecting aviation
-
Heat Exchange Processes
Fluid Mechanics
-
fluid theory
-
temperature and energy distributions
-
Analysis Of Experimental Uncertainty
Objectives
-
Nature and different properties of fluids
-
Internal and external flows
-
Analysis of engineering applications of incompressible pipe systems
Aircraft Structure and Construction
-
Composites in aircraft
-
Transparent plastics
-
Dope and fabric aircraft
Objectives
-
The mechanism and process of building an aircraft
-
Aircraft structural construction methods
-
Practices and terminology
Certification
Once a candidate is done with their bachelor’s degree, pilots will need to obtain a private pilot certificate. As per the FAA, pilots have a minimum of 40 flight hours. The most ideal place to get certified training are schools that are overseen by the FAA. They offer the highest quality training programs that have highly structured phases of learning.
After obtaining a private pilot license, a pilot must obtain an instrument rating and commercial certificate which is necessary for any pilot who wants to be paid for flying passengers or cargo. A pilot must have at least 50 flying hours of Pilot in Command flying across the country in order to obtain an instrument rating. For a commercial certificate, a pilot is required to fly 250 hours of time including 100 hours of PIC, 50 hours of cross country flying, and a minimum of 10 hours of learning inside of a complex aircraft.
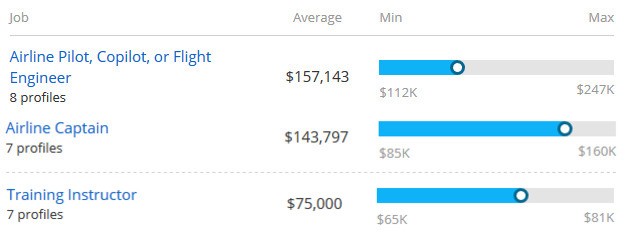
Salary of a Pilot
While each airline has its own pay schedule, nearly all airlines offer standard hikes annually. Pilots experience their biggest salary increase in the first five years of their careers. Interestingly, this increase is often larger for first officers than for pilots with the largest hike occurring after a year of a probationary period.
Depending on the airline, type of aircraft, and the pilot’s experience level, a regional pilot typically starts out making $20 - $50 per hour or about $20,000 to $40,000 per year. Additionally, a pilot receives a stipend during the training period as well as per diem rate when away from home.
The average annual salary of a large jet pilot is around $122000, while small jet pilots earn an average salary of $105000. Non-jet aircraft pilots make significantly as compared to their peers flying jet aircraft. For a large non-jet pilot, the average annual salary is $79,000 and for a small non-jet aircraft pilot, the average annual salary is $85,500.
Job Growth of a Pilot
According to a report by BLS, the overall employment of airline and commercial pilots is projected to grow at an average rate of 6% from 2018 to 2028. Most job opportunities are expected to arise from the need to replace pilots who retire or leave the occupation permanently over the projection period.
Most pilots commence their career as a first officer and it takes anywhere for a first officer five to fifteen years to become a pilot. Depending on the skill proficiencies, a first officer is promoted to the post of the pilot. Bigger airline companies have opportunities for further positions. Depending on the number of years of work experience as a pilot, a candidate can be promoted to the position of director of chief pilot.
Job Concentrations for a pilot
Following are the job concentrations for a pilot,
Aircraft Pilot: The most common job concentration is to become an aircraft pilot. There are 2 types of aircraft pilot- commercial and cargo. In addition to flying and navigating air transportation, an aircraft pilot is also responsible for quality assurance before and after flights. A pilot has to have an understanding of meteorology to anticipate and address weather-related problems
Academician: Those that want to get into the field of academics and research have to pursue a doctoral degree program in the subject they intend to teach. Profs in the aeronautical field teach curriculums in engineering, design, theory, and flight. They teach students the fundamental principles of aerospace and systems related to flight
Air Traffic Controller: air traffic controllers ensure the safety of the aircraft by monitoring operations in the air and on land. ATCs help aircraft stay on course and maintain safe distances during flight, take-off, and landings.
Stand out skills for a Pilot
The following skills will help you stand out as a Pilot :
Good interpersonal and communication skills: A pilot has to be constantly in touch with the ground air control, the cabin crew, and the passengers and even a slight miscommunication can lead to risking the lives of passengers and crew on board. Hence, it is important that the pilot has good communication skills for the smooth flying of the airplane.
Teamwork and leadership skills: The pilot is in charge and in command of the flight. Hence it is important to show leadership skills as the pilot is responsible for making all the final calls. Being able to work as a team with the crew, coordinating and assigning tasks, and working alongside a co-pilot are few of the KRAs of a pilot. It requires the pilot to have a spirit of teamwork.
Good Mathematical and physics skills: A pilot needs to be able to calculate and design flight routes and fuel consumption plans. This is where mathematics and physics come into play. A pilot must possess excellent mathematical and physics skills.
Stress management and decision making skills: having good stress management skills will help in moments of high stress. This will help the pilot remain calm and focussed. In case of emergencies, a pilot must be able to assess the situation and handle the situation in a timely manner. To be able to make quick and effective decisions is one of the most important skills to become successful as a pilot.
Good understanding of Mechanical and flight engineering: A pilot must have a good understanding of mechanical and flight engineering. A pilot must be capable of running system inspections, fixing minor problems if needed and have a good understanding of the basic and complex concepts of airplane systems
Good Stamina and physical condition: One of the most important skills for a pilot is to have good stamina. A pilot must possess the stamina for flying an aircraft through long routes and have excellent vision and hearing abilities. It is important to note that pilots should not suffer from cardiac conditions.
| Minumum Credit Score | Apply in as little as | Variable APR | Fixed APR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | Not Available | 15 minutes or less | 2.95 | 4.74 | View disclosures |
 | 620 | 2 minutes | 5.38%-16.99%1 | 4.43%-16.99%1 | View disclosures |
 | Not Available | 15 minutes | 1.13% - 11.23%¹ (with autopay) | 3.50% - 12.60%¹ (with autopay) | View disclosures |